Tut ench amun
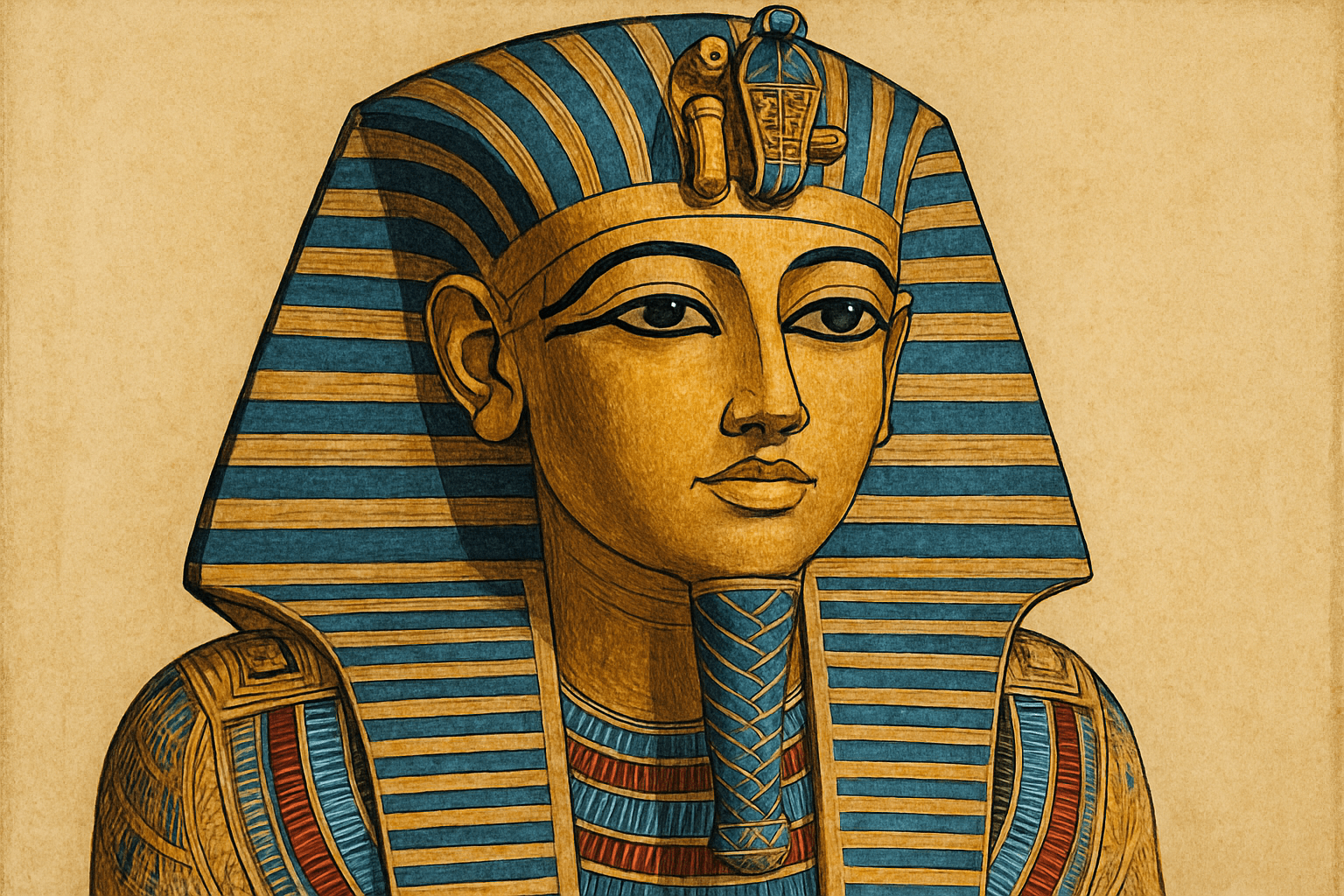
The art style of Tutankhamun is characterized by its use of bright colors and bold patterns. The art is often geometric in nature, and often features animals and gods.
AOI thinking about Tut ench amun [+_~]-/
Overview and Quickfacts
Tutankhamun’s art style is characterized by its use of bright colors and ornate details. It is a highly stylized form of art that often uses symbolism to communicate its message. Tutankhamun’s art is often associated with the Egyptian god Horus, and it is believed that Tutankhamun’s art style was inspired by the art of the Amarna period.
Can understand it also, as:
King Tut, Tutankhamun
Categorize it as:
Impressionism, Modernism
.: Dreaming :.
holds a HAIKU for the art style
:. Thought is power .:
Detailed Description
Tutankhamun, also known as King Tut, was an Egyptian pharaoh who ruled from 1332 to 1323 BC. He was the last of the line of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt’s New Kingdom. His original name was Tutankhaten, meaning “Living Image of Aten”, but he changed it to Tutankhamun when he restored the worship of the god Amun. Tutankhamun is best known for the discovery of his tomb by Howard Carter in 1922. His tomb was the only one from the Valley of the Kings to have escaped the ravages of tomb robbers. It contained the richest collection of ancient Egyptian artifacts ever found, including the famous gold mask of Tutankhamun. Tutankhamun was a small man, less than five feet tall. He had a clubfoot, and his left arm was slightly deformed. He also had a genetic disorder called Marfan syndrome, which caused him to have an elongated skull. Despite his physical abnormalities, Tutankhamun was a skilled warrior and hunter. He was also a talented musician and composer. The art style of Tutankhamun is characterized by its use of bright colors and ornate designs. Tutankhamun’s tomb paintings are some of the most beautiful and well-preserved examples of ancient Egyptian art. Some of the most famous Tutankhamun paintings include the scenes from his tomb, such as the one depicting his funeral procession. Other famous paintings include the ones depicting Tutankhamun hunting lions and elephants. Tutankhamun’s art style was heavily influenced by the art of the Amarna period, which was characterized by its use of naturalistic and realistic depictions of people and animals. Tutankhamun’s art style is also unique in its use of portraiture. Unlike other Egyptian pharaohs, Tutankhamun is shown in his paintings as a real person, with all of his physical imperfections on full display. This realistic approach to portraiture was likely inspired by Tutankhamun’s own physical abnormalities. By depicting himself as he really was, Tutankhamun was able to create a more personal connection with his subjects. The art style of Tutankhamun has had a lasting impact on the world of art. Tutankhamun’s tomb paintings are some of the most iconic images of ancient Egypt, and his use of bright colors and realistic portraiture has influenced artists for centuries.
.. beep, beep, beep ..
<START OF TRANSMISSION>
1. Tutankhamun was an Egyptian pharaoh of the 18th dynasty, during the period of Egyptian history known as the New Kingdom. 2. He is popularly referred to as King Tut. 3. Tutankhamun was the son of Akhenaten and an unknown mother. 4. He became pharaoh at the age of nine, after his father's death. 5. Tutankhamun reigned for approximately ten years. 6. He was married to his half-sister, Ankhesenamun. 7. Tutankhamun is best known for the discovery of his intact tomb by Howard Carter in 1922. 8. Tutankhamun's tomb is the most intact royal tomb ever found in Egypt. 9. Tutankhamun was buried in a tomb that was originally intended for someone else. 10. The cause of Tutankhamun's death is unknown. 11. Tutankhamun's mummy was in an poor condition when it was discovered. 12. It is believed that Tutankhamun was around eighteen years old at the time of his death. 13. The tomb of Tutankhamun is located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt. 14. Tutankhamun's tomb is the only royal tomb that has been found in the Valley of the Kings that is intact. 15. Tutankhamun's tomb is the smallest of all the royal tombs in the Valley of the Kings. 16. The tomb of Tutankhamun is the only royal tomb that has been found in the Valley of the Kings that is not plundered. 17. The tomb of Tutankhamun is the only royal tomb that has been found in the Valley of the Kings that is not vandalized. 18. The tomb of Tutankhamun is the only royal tomb that has been found in the Valley of the Kings that is not damaged. 19. The tomb of Tutankhamun is the only royal tomb that has been found in the Valley of the Kings that is not destroyed. 20. The tomb of Tutankhamun is the only royal tomb that has been found in the Valley of the Kings that is not missing any of its contents.
<EOF>
.. robbel bob
Visual Examples from our image gallery
Coming soon, we are so slow .. might never come
Artists, Paintings, and more
(be aware, can be highly speculative)
Artists (be aware, speculation possible):
1. Akhenaten ÃÂÃÂ 1353 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1336 BC 2. Nefertiti ÃÂÃÂ 1370 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1330 BC 3. Tutankhamun ÃÂÃÂ 1341 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1323 BC 4. Ay ÃÂÃÂ 1327 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1323 BC 5. Horemheb ÃÂÃÂ 1319 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1292 BC 6. Seti I ÃÂÃÂ 1318 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1290 BC 7. Ramesses II ÃÂÃÂ 1279 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1213 BC 8. Merneptah ÃÂÃÂ 1213 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1203 BC 9. Seti II ÃÂÃÂ 1204 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1194 BC 10. Twosret ÃÂÃÂ 1191 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1189 BC 11. Siptah ÃÂÃÂ 1189 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1187 BC 12. Setnakhte ÃÂÃÂ 1186 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1184 BC 13. Ramesses III ÃÂÃÂ 1184 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1153 BC 14. Ramesses IV ÃÂÃÂ 1153 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1147 BC 15. Ramesses V ÃÂÃÂ 1147 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1143 BC 16. Ramesses VI ÃÂÃÂ 1143 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1136 BC 17. Ramesses VII ÃÂÃÂ 1136 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1129 BC 18. Ramesses VIII ÃÂÃÂ 1129 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1126 BC 19. Ramesses IX ÃÂÃÂ 1126 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1107 BC 20. Ramesses X ÃÂÃÂ 1107 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1077 BC 21. Ramesses XI ÃÂÃÂ 1077 BC ÃÂÃÂ 1047 BC 22. Smendes ÃÂÃÂ 1047 BC ÃÂÃÂ 945 BC 23. Amenemnisu ÃÂÃÂ 945 BC ÃÂÃÂ 924 BC 24. Psusennes I ÃÂÃÂ 924 BC ÃÂÃÂ 887 BC 25. Amenemope ÃÂÃÂ 887 BC ÃÂÃÂ 858 BC 26. Osorkon the Elder ÃÂÃÂ 858 BC ÃÂÃÂ 833 BC 27. Shoshenq I ÃÂÃÂ 833 BC ÃÂÃÂ 773 BC 28. Osorkon II ÃÂÃÂ 773 BC ÃÂÃÂ 749 BC 29. Takelot I ÃÂÃÂ 749 BC ÃÂÃÂ 716 BC 30. Pedubast I ÃÂÃÂ 716 BC ÃÂÃÂ 702 BC
Artworks (be aware, speculation possible)
1. Tutankhamun and His Wife (c. 1340 BC) 2. Tutankhamun and the Golden Throne (c. 1340 BC) 3. Tutankhamun’s Funeral Mask (c. 1323 BC) 4. Tutankhamun’s Tomb Painting (c. 1323 BC) 5. Tutankhamun’s Sarcophagus (c. 1323 BC) 6. The Death of Tutankhamun (c. 1323 BC) 7. The Burial of Tutankhamun (c. 1323 BC) 8. The Opening of Tutankhamun’s Tomb (c. 1922) 9. The Mummy of Tutankhamun (c. 1924) 10. Tutankhamun’s Treasures (c. 1925) 11. The Golden Mask of Tutankhamun (c. 1925) 12. The Golden Coffin of Tutankhamun (c. 1925) 13. The Jewelry of Tutankhamun (c. 1925) 14. The Statues of Tutankhamun (c. 1925) 15. The Canopic Jars of Tutankhamun (c. 1925) 16. The Sarcophagus of Tutankhamun (c. 1925) 17. The Mummy of Tutankhamun (c. 1926) 18. The Funeral Mask of Tutankhamun (c. 1926) 19. The Golden Mask of Tutankhamun (c. 1926) 20. The Golden Coffin of Tutankhamun (c. 1926) 21. The Sarcophagus of Tutankhamun (c. 1926) 22. The Burial Chamber of Tutankhamun (c. 1926) 23. The Tomb of Tutankhamun (c. 1926) 24. The Treasures of Tutankhamun (c. 1926) 25. The Mummy of Tutankhamun (c. 1927) 26. The Funeral Mask of Tutankhamun (c. 1927) 27. The Golden Mask of Tutankhamun (c. 1927) 28. The Golden Coffin of Tutankhamun (c. 1927) 29. The Sarcophagus of Tutankhamun (c. 1927) 30. The Tomb of Tutankhamun (c. 1927)
Epoch
The art style of Tutankhamun is associated with the 18th dynasty of Egypt, which lasted from 1550-1292 BCE.
AI ART RESSOURCES (AKA, well Tools)
Helping tools -> predefined search links on other pages: