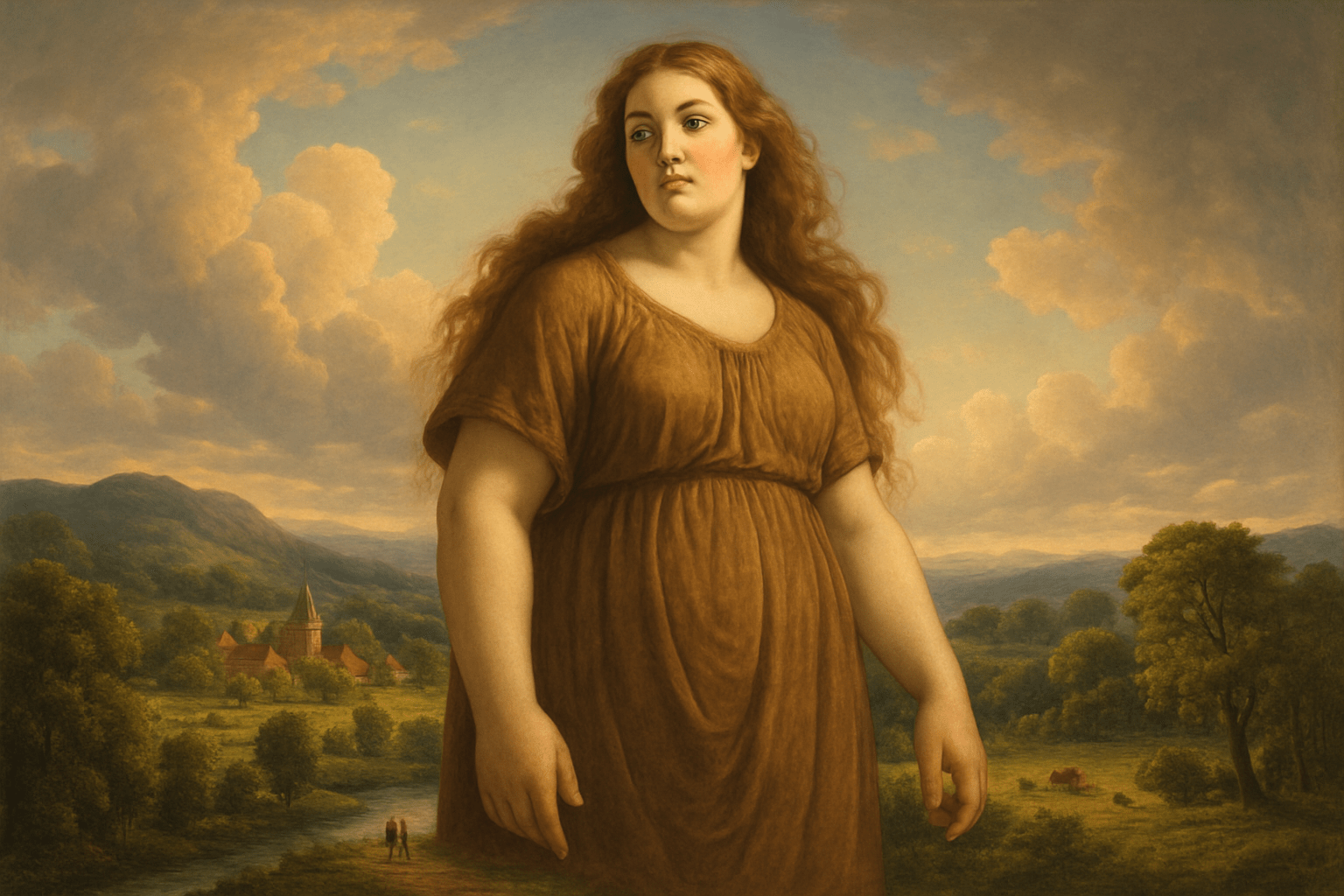
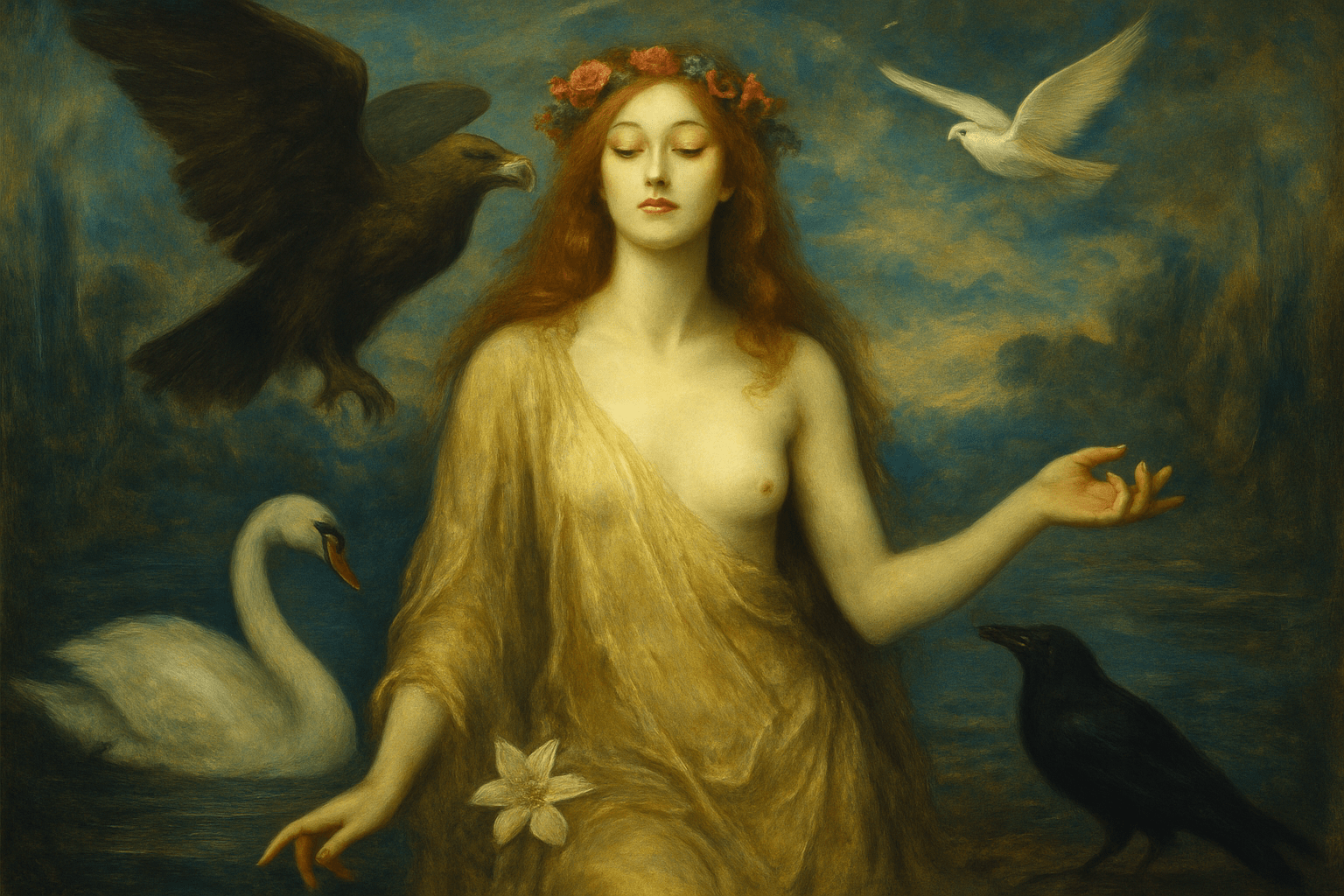Symbolism
The art style Symbolism is characterized by its use of symbols to represent ideas or concepts. These symbols can be literal or figurative, and are often used to convey a message or feeling. Symbolist art is often dark or mysterious, and often has a dreamlike quality.
AOI thinking about Symbolism [+_~]-/
Overview and Quickfacts
Symbolism was a late nineteenth-century art movement of French, Russian and Belgian origin in poetry and other arts. In literature, the style originates with the 1857 publication of Charles Baudelaire’s Les Fleurs du mal. The works of Edgar Allan Poe, which Baudelaire admired greatly and translated into French, were a significant influence and the source of many stock tropes and images. The aesthetic was developed by a group of poets, critics and artists associated with Les Vingt, in Brussels and Paris.
Can understand it also, as:
Metaphor, simile, allegory, emblem, sign
Categorize it as:
Impressionism, Modernism
.: Dreaming :.
holds a HAIKU for the art style
:. Thought is power .:
Detailed Description
Symbolism was a late nineteenth-century art movement of French, Russian and Belgian origin in poetry and other arts. In literature, the style originates with the 1857 publication of Charles Baudelaire’s Les Fleurs du mal; the works of Edgar Allan Poe, which Baudelaire admired greatly and translated into French, were a significant influence and the source of many stock tropes and images. The aesthetic was developed by a group of poets and artists associated with the Salon de la Rose+Croix in Paris, although Symbolism as an art movement preceded the Salon. Due to the fact that Symbolism focused more on ideas and emotions rather than on concrete reality, it was considered by some to be a reaction against Impressionism and Naturalism, while others believed that it was the logical continuation of the Romantic tradition. In a broad sense, Symbolism was a reaction against the materialism and empiricism which dominated the arts in the 19th century. Symbolists believed that art should represent absolute truths that could only be described indirectly; thus, they wrote in a highly metaphorical and suggestive manner, using symbols and images to convey complex ideas and emotions. In this respect, they were influenced by the Pre-Raphaelites, who sought to express spiritual truths through the depiction of physical reality. The Symbolist aesthetic was characterized by a highly subjective, personal style; the artists sought to express their innermost thoughts and emotions rather than to record objective reality. The chief characteristics of Symbolist art are suggestiveness and ambiguity, both of which are achieved through the use of symbols. Symbolist artists believed that art should express the innermost truths of the human soul, and that these truths could only be hinted at indirectly; thus, they often used symbols to suggest ideas and emotions. Famous Symbolist artists include Odilon Redon, Gustave Moreau, Paul Gauguin, and Aubrey Beardsley.
.. beep, beep, beep ..
<START OF TRANSMISSION>
1. Symbolism is the use of symbols to represent ideas or qualities. 2. Symbols can be used to represent concepts, emotions, or physical objects. 3. Symbols can be literal or figurative. 4. Literal symbols are those that represent an object or concept directly. For example, a heart symbolizes love. 5. Figurative symbols are those that represent an object or concept indirectly. For example, a rose may symbolize love, passion, or sacrifice. 6. Symbols can be universal or culture-specific. 7. Universal symbols are those that are understood by people across cultures. For example, a cross symbolizes Christianity. 8. Culture-specific symbols are those that are specific to a certain culture. For example, a dragon symbolizes China. 9. Symbols can be static or dynamic. 10. Static symbols are those that remain the same over time. For example, a flag is a static symbol of a country. 11. Dynamic symbols are those that change over time. For example, a person's hairstyle may be a dynamic symbol of their identity. 12. Symbols can be natural or man-made. 13. Natural symbols are those that occur in nature. For example, a tree may symbolize growth. 14. Man-made symbols are those that are created by humans. For example, a building may symbolize power. 15. Symbols can be concrete or abstract. 16. Concrete symbols are those that can be seen or touched. For example, a statue is a concrete symbol of a person. 17. Abstract symbols are those that cannot be seen or touched. For example, a sound may symbolize a feeling. 18. Symbols can be positive or negative. 19. Positive symbols are those that represent something good. For example, a smile may symbolize happiness. 20. Negative symbols are those that represent something bad. For example, a skull may symbolize death.
<EOF>
.. robbel bob
Visual Examples from our image gallery
Coming soon, we are so slow .. might never come
Artists, Paintings, and more
(be aware, can be highly speculative)
Artists (be aware, speculation possible):
1. William Blake (1757-1827) 2. John Martin (1789-1854) 3. Edward Robert Hughes (1851-1914) 4. William Morris (1834-1896) 5. Dante Gabriel Rossetti (1828-1882) 6. James Abbott McNeill Whistler (1834-1903) 7. Arnold BÃÂöcklin (1827-1901) 8. Max Klinger (1857-1920) 9. Odilon Redon (1840-1916) 10. Gustave Moreau (1826-1898) 11. Henri Fantin-Latour (1836-1904) 12. Paul Gauguin (1848-1903) 13. Georges Seurat (1859-1891) 14. Camille Pissarro (1830-1903) 15. Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1841-1919) 16. Paul CÃÂézanne (1839-1906) 17. Vincent van Gogh (1853-1890) 18. Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec (1864-1901) 19. Georges MÃÂéliÃÂès (1861-1938) 20. Emile Cohl (1857-1938) 21. Winsor McCay (1867-1934) 22. George Herriman (1880-1944) 23. Otto Messmer (1892-1983) 24. Walt Disney (1901-1966) 25. Ub Iwerks (1901-1971) 26. Max Fleischer (1883-1972) 27. Chuck Jones (1912-2002) 28. John Kricfalusi (1955- ) 29. Matt Groening (1954- ) 30. Mike Judge (1962- )
Artworks (be aware, speculation possible)
1. The Scream, Edvard Munch, 1893 2. The Starry Night, Vincent van Gogh, 1889 3. The Persistence of Memory, Salvador DalÃÂÃÂ, 1931 4. Nighthawks, Edward Hopper, 1942 5. The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari, Robert Wiene, 1920 6. The Great Wave off Kanagawa, Katsushika Hokusai, 1829-32 7. The Hay Wagon, Andrew Wyeth, 1953 8. American Gothic, Grant Wood, 1930 9. The Madonna of the Stairs, Michelangelo, 1501-04 10. The Creation of Adam, Michelangelo, 1511 11. The Last Supper, Leonardo da Vinci, 1498 12. The Birth of Venus, Sandro Botticelli, 1486 13. The Madonna and Child, Leonardo da Vinci, c. 1472 14. The Annunciation, Leonardo da Vinci, c. 1472 15. The Baptism of Christ, Leonardo da Vinci, 1472-75 16. The Adoration of the Magi, Leonardo da Vinci, 1481-82 17. The Madonna of the Rocks, Leonardo da Vinci, c. 1483 18. The Mona Lisa, Leonardo da Vinci, c. 1503-06 19. The Girl with a Pearl Earring, Johannes Vermeer, c. 1665 20. The Night Watch, Rembrandt, 1642 21. The Hay Wagon, Andrew Wyeth, 1953 22. The Arnolfini Portrait, Jan van Eyck, 1434 23. The Ghent Altarpiece, Jan van Eyck, 1432 24. The Madonna and Child, Michelangelo, 1497-98 25. The Sistine Chapel Ceiling, Michelangelo, 1508-12 26. The Last Supper, Leonardo da Vinci, 1498 27. The Birth of Venus, Sandro Botticelli, 1486 28. The Annunciation, Leonardo da Vinci, c. 1472 29. The Baptism of Christ, Leonardo da Vinci, 1472-75 30. The Madonna of the Rocks, Leonardo da Vinci, c. 1483
Epoch
The Symbolism art movement was active from roughly 1886 to 1910.
AI ART RESSOURCES (AKA, well Tools)
Helping tools -> predefined search links on other pages: