Japonism
The art style Japonism is characterized by its use of bright colors and bold patterns. It is often inspired by traditional Japanese art, and often incorporates elements of nature into its designs.
AOI thinking about Japonism [+_~]-/
Overview and Quickfacts
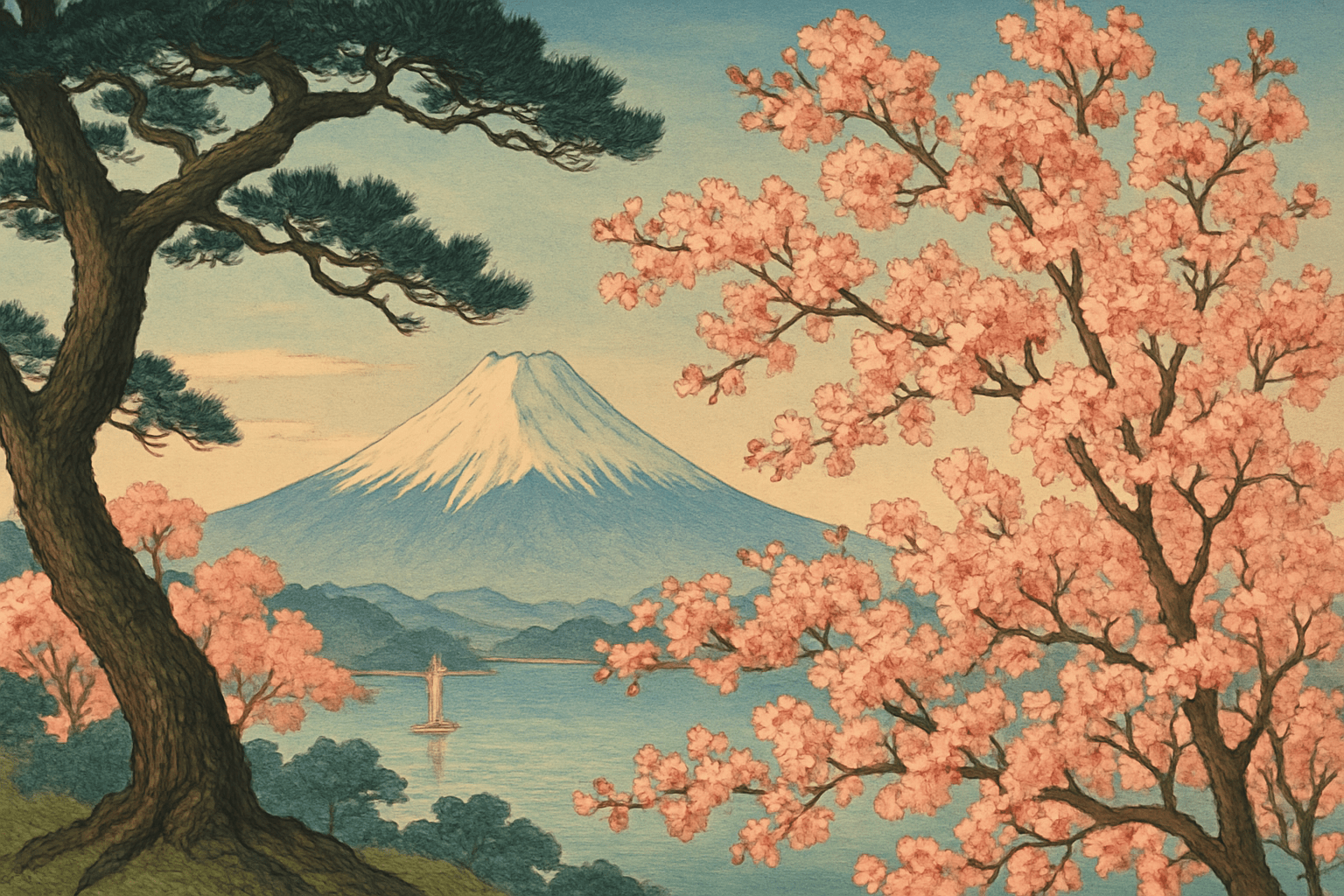
Japonism is a Western art movement that began in the late 19th century as a response to the influx of Japanese art and artifacts that were being brought into Europe. Japonisme, as it was called in France, was characterized by an interest in Japanese aesthetics and an appreciation for the simplicity and elegance of Japanese art and design. During the Meiji period in Japan (1868-1912), there was a dramatic increase in Western trade and influence, which led to a corresponding increase in the importation of Western goods into Japan. This included a wide variety of art objects, including painting, sculpture, and ceramics. Many of these objects found their way into the hands of European collectors and artists, who were fascinated by the unfamiliar aesthetics of Japanese art. Japonism had a profound impact on Western art, particularly in the areas of painting and design. Impressionist painters such as Claude Monet and Pierre-Auguste Renoir were deeply influenced by Japanese woodblock prints, and used them as sources of inspiration for their own work. In the field of design, Japonisme was a major force behind the Art Nouveau movement. Today, the influence of Japonism can still be seen in many areas of Western art and design.
Can understand it also, as:
Japanese art, culture, and aesthetics; the influence of Japanese art on Western art
Categorize it as:
Impressionism, Modernism
.: Dreaming :.
holds a HAIKU for the art style
:. Thought is power .:
Detailed Description
Japonism is a Western art movement that started in the late 19th century. It is characterized by an interest in Japanese art, culture, and aesthetics. One of the first Westerners to visit Japan was the Dutch artist, Isaac de Graeff. He was impressed by the country’s art and culture and wrote about his experiences in a book called “The Land of the Rising Sun.” This book sparked interest in Japan among Western artists and intellectuals. During the Meiji period (1868-1912), Japan underwent a rapid modernization process. This led to a surge in Western interest in Japanese art and culture. Many Western artists and intellectuals visited Japan during this time. One of the most famous Western artists to be influenced by Japonism is Claude Monet. He was captivated by the country’s landscapes and gardens and painted many famous works inspired by his visits to Japan. Other notable Western artists who were influenced by Japonism include Vincent van Gogh, Paul Gauguin, and Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec. Japonism had a significant impact on Western art and culture. It introduced new ideas and aesthetics that were influential in the development of modern art.
.. beep, beep, beep ..
<START OF TRANSMISSION>
1. Japonism is a Western term for the influence of Japanese art, culture, and aesthetics on Western art, beginning in the 19th century. 2. Japonism reached its peak in the late 19th century, coinciding with Japan's opening of trade with the West and a growing fascination with all things Japanese. 3. Western artists who were influenced by Japonism include Claude Monet, Edgar Degas, Vincent van Gogh, and Paul Gauguin. 4. Japonism had a significant impact on Western art movements such as Impressionism, Post-Impressionism, and Art Nouveau. 5. Japanese art was characterized by its simplicity, elegance, and serenity, which contrasted sharply with the ornate, dramatic style of Western art. 6. Japonism also introduced new subjects and themes to Western art, such as nature scenes, landscapes, and scenes from daily life. 7. Japanese prints were particularly popular among Western artists, who were fascinated by their bold colors and striking compositions. 8. Many Western artists who were influenced by Japonism visited Japan, including Monet, who made several trips in the late 1800s. 9. The popularity of Japonism began to decline in the early 20th century, as Western artists increasingly turned to other sources of inspiration. 10. However, Japonism has continued to exert a significant influence on Western art in the post-war period, particularly on movements such as Abstract Expressionism. 11. Japonism has also been an important influence on fashion, design, and popular culture in the West. 12. The term "Japonism" was first coined by the French art critic Philippe Burty in 1872. 13. The word "Japonisme" was first used in English in 1878 by the art historian Edward Dillon. 14. The term "Japonism" is sometimes used interchangeably with "Japanism," although the latter term is more commonly used in Japan. 15. Japonism is not to be confused with "Japonisme," which refers to the study of Japanese culture and society by Western scholars. 16. Japonism is also distinct from "Japanophilia," which is a general love or admiration for Japan and things Japanese. 17. Japonism is sometimes referred to as "the Japanese virus," due to its perceived ability to infect and corrupt Western art. 18. Japonism has been criticized for promoting stereotypes of Japan and Japanese culture, and for contributing to the Westernization of Japan. 19. Some Japanese artists and intellectuals have also critiqued Japonism, arguing that it has led to a loss of traditional Japanese values. 20. Despite its critics, Japonism continues to be a significant and influential force in the world of art and culture.
<EOF>
.. robbel bob
Visual Examples from our image gallery
Coming soon, we are so slow .. might never come
Artists, Paintings, and more
(be aware, can be highly speculative)
Artists (be aware, speculation possible):
X
Artworks (be aware, speculation possible)
X
Epoch
X
AI ART RESSOURCES (AKA, well Tools)
Helping tools -> predefined search links on other pages: