Photorealism
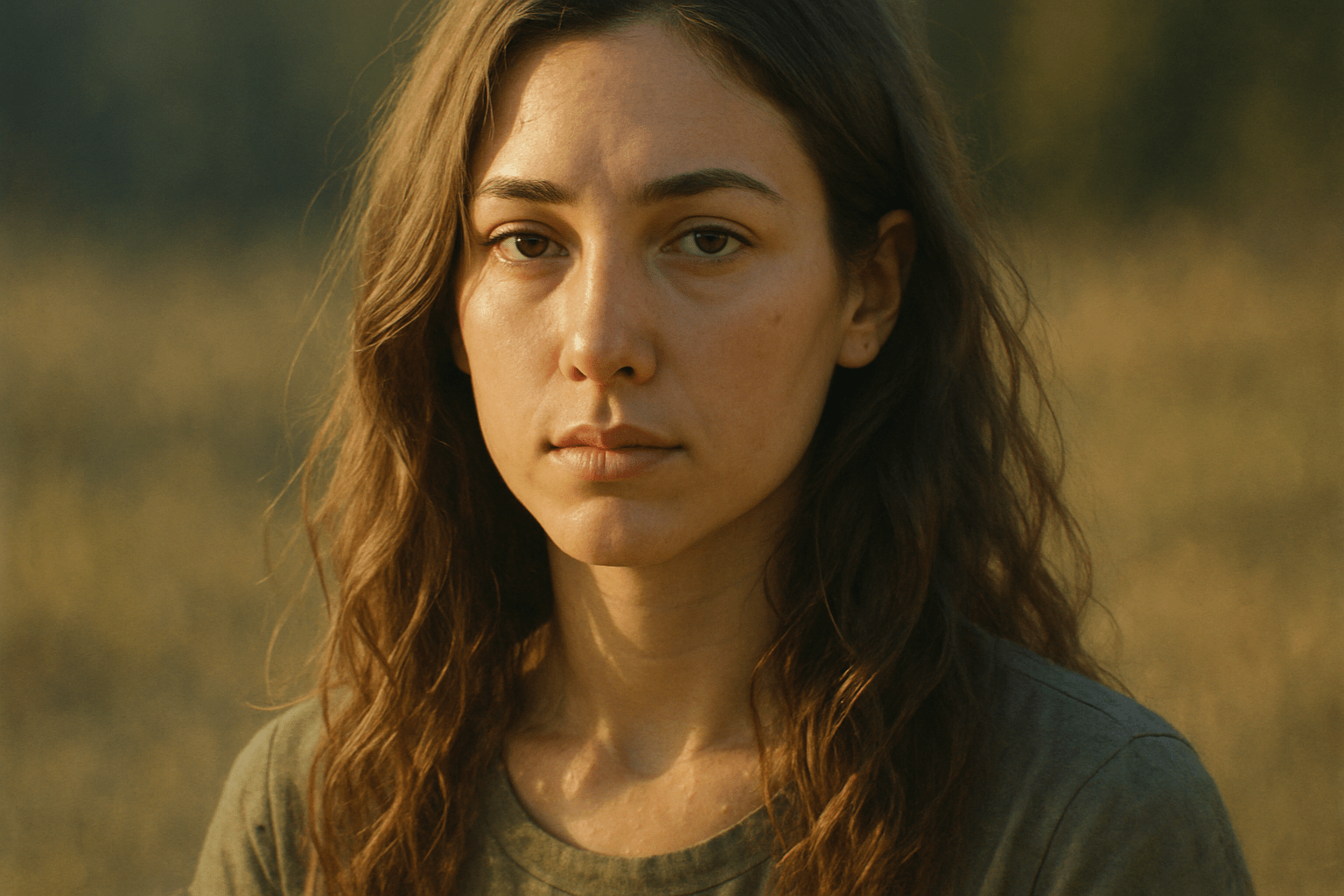
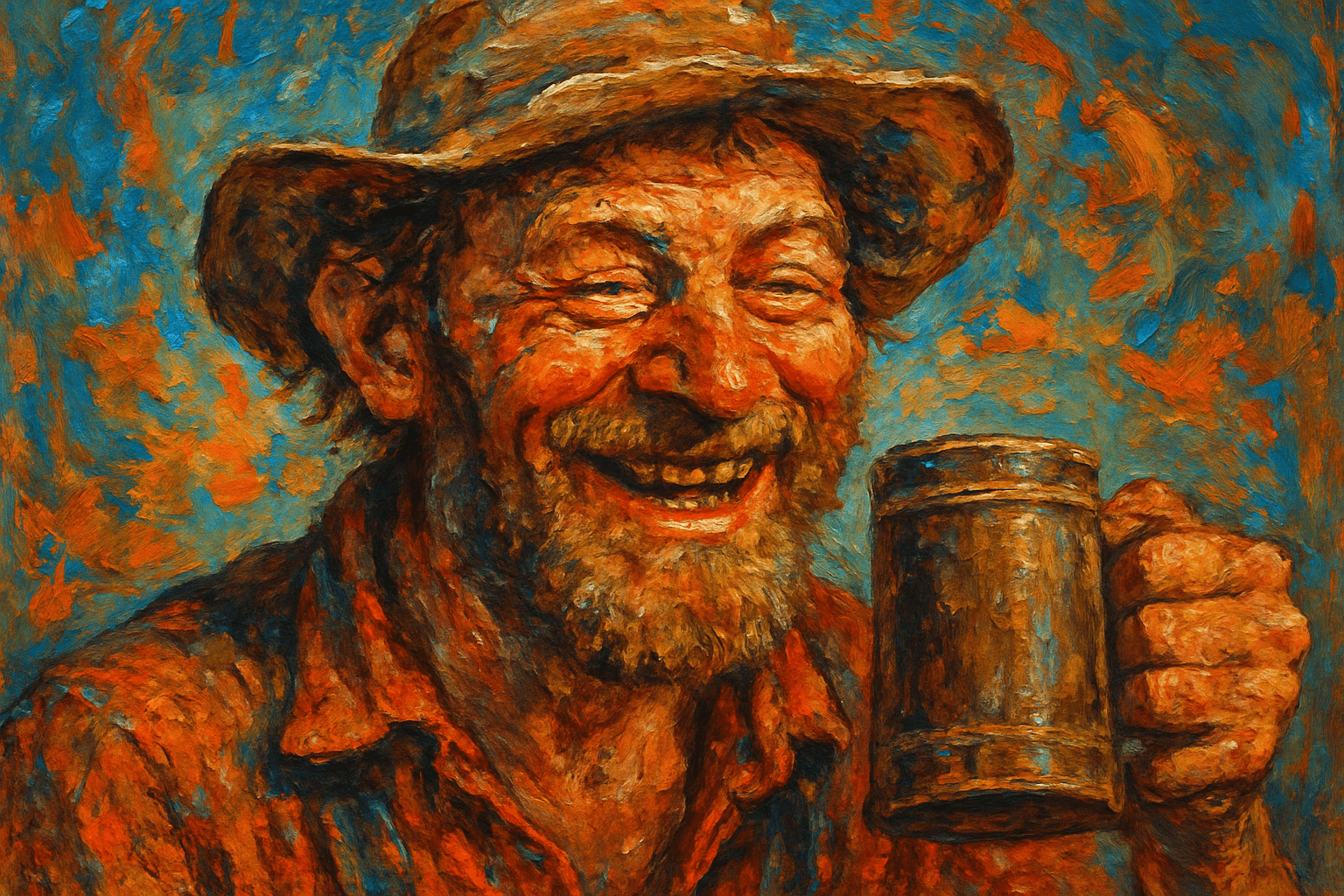
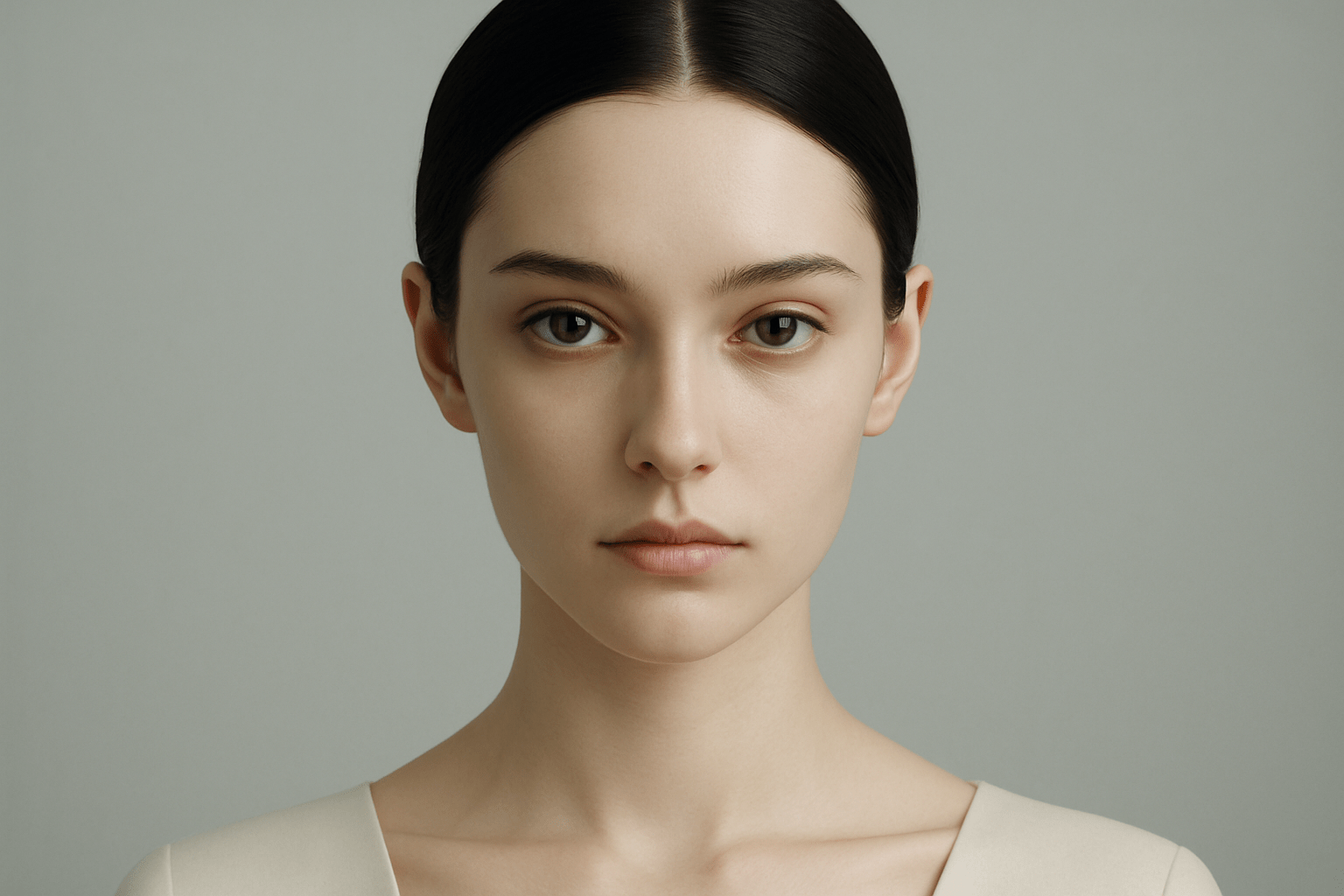
The art style of Photorealism is characterized by its extremely realistic visual appearance. This is achieved through the use of high-resolution images and the careful use of light and shadow to create a realistic three-dimensional effect.
AOI thinking about Photorealism [+_~]-/
Overview and Quickfacts
Photorealism is a genre of painting that combines high-resolution images and advanced printing techniques to create incredibly lifelike artworks. Photorealistic paintings are often mistaken for photographs, but they are actually hand-painted or airbrushed works of art. This highly realistic style emerged in the late 1960s and early 1970s, and it continues to be popular among artists and collectors today.
Can understand it also, as:
Realism, naturalism, lifelike, true to life
Categorize it as:
Impressionism, Modernism
.: Dreaming :.
holds a HAIKU for the art style
:. Thought is power .:
Detailed Description
Photorealism is a genre of painting that combines extreme precision with a realistic style. It is often mistaken for photography because of its incredibly lifelike qualities. Photorealism began in the late 1960s and early 1970s, and its popularity grew throughout the following decade. Many of the original photorealist painters were American, but the movement quickly spread to Europe and beyond. Famous photorealist painters include Chuck Close, Richard Estes, Audrey Flack, and John Baeder. Close is perhaps the most well-known photorealist painter, and his large-scale portraits are instantly recognizable. Estes is known for his cityscapes, which capture the hustle and bustle of urban life. Flack is celebrated for her still lifes, which often incorporate found objects. Baeder is known for his paintings of diners and other roadside attractions. While photorealism is often associated with painting, the genre has also been explored by photographers and sculptors. Photorealistic sculptures are often incredibly lifelike, and can fool even the most discerning viewer. Notable photorealistic sculptors include Duane Hanson and John De Andrea. If you’re interested in exploring photorealism further, there are many excellent resources available. The Photorealism Research Center is a great place to start.
.. beep, beep, beep ..
<START OF TRANSMISSION>
1. Photorealism is a genre of painting that depicts realistic scenes as they would appear in a photograph. 2. Photorealist paintings are often mistaken for photographs. 3. The term "photorealism" was coined by art critic Don Judd in 1968. 4. Photorealism developed in the United States in the late 1960s and early 1970s. 5. The first photorealist paintings were often of urban landscapes. 6. Photorealism is sometimes confused with hyperrealism. 7. While both genres strive for realism, photorealism is more concerned with the accurate depiction of light and shadow, whereas hyperrealism often incorporates elements of fantasy or the surreal. 8. Notable photorealist painters include Richard Estes, Chuck Close, and Audrey Flack. 9. Photorealism has been criticized for its lack of emotion and for being "cold" and "clinical." 10. Some photorealist paintings are created using a grid system, where the artist enlarges a photograph and then paints it, one square at a time. 11. The use of a grid system was popularized by Chuck Close, who has used it in many of his photorealist portraits. 12. Many photorealist painters use a technique called "slip-sliding," where they paint over a photograph, moving the paint back and forth until the desired effect is achieved. 13. Photorealism often relies heavily on the use of photo reference material. 14. Some photorealist painters have been accused of "stealing" their images from photographs. 15. Photorealism is sometimes seen as a reaction against the abstract expressionism of the 1950s and 1960s. 16. Many photorealist painters were formally trained as photographers. 17. The use of airbrushing is often associated with photorealism. 18. Photorealism has been described as "the dead end of painting." 19. In recent years, photorealism has experienced a resurgence in popularity. 20. Some critics argue that the rise of digital photography has made photorealism obsolete.
<EOF>
.. robbel bob
Visual Examples from our image gallery
Coming soon, we are so slow .. might never come
Artists, Paintings, and more
(be aware, can be highly speculative)
Artists (be aware, speculation possible):
1. John Baeder (born 1942) 2. Richard Estes (born 1932) 3. Chuck Close (born 1940) 4. Don Eddy (born 1943) 5. Tom Blackwell (born 1935) 6. Audrey Flack (born 1931) 7. Robert Bechtle (born 1932) 8. Richard McLean (born 1944) 9. Robert Cottingham (born 1935) 10. Stanley Meltzoff (born 1917) 11. William Eggleston (born 1939) 12. Walker Evans (1903-1975) 13. Lee Friedlander (born 1934) 14. Garry Winogrand (1928-1984) 15. Joel Meyerowitz (born 1938) 16. Elliot Erwitt (born 1928) 17. Diane Arbus (1923-1971) 18. Bruce Gilden (born 1946) 19. Mary Ellen Mark (1940-2015) 20. Nan Goldin (born 1953) 21. William Wegman (born 1943) 22. Cindy Sherman (born 1954) 23. Andreas Gursky (born 1955) 24. Jeff Wall (born 1946) 25. Gregory Crewdson (born 1962) 26. James Welling (born 1951) 27. Thomas Ruff (born 1958) 28. Bernd and Hilla Becher (1931-2007 and 1934-2015, respectively) 29. Hiroshi Sugimoto (born 1948) 30. Thomas Struth (born 1954)
Artworks (be aware, speculation possible)
1. “Nighthawks” by Edward Hopper (1942) 2. “American Gothic” by Grant Wood (1930) 3. “The Hay Wagon” by Andrew Wyeth (1965) 4. ” Christina’s World” by Andrew Wyeth (1948) 5. “One Nation…” by James Rosenquist (1986) 6. “The Drowning Girl” by Roy Lichtenstein (1963) 7. “Whaam!” by Roy Lichtenstein (1963) 8. “Nude Descending a Staircase, No. 2” by Marcel Duchamp (1912) 9. “Fountain” by Marcel Duchamp (1917) 10. “L.H.O.O.Q.” by Marcel Duchamp (1919) 11. “Portrait of Adele Bloch-Bauer I” by Gustav Klimt (1907) 12. “The Kiss” by Gustav Klimt (1908) 13. “Birch Forest” by Ernst Ludwig Kirchner (1908) 14. “Street, Dresden” by Ernst Ludwig Kirchner (1908) 15. “Self-Portrait as a Soldier” by Ernst Ludwig Kirchner (1915) 16. “The Scream” by Edvard Munch (1895) 17. “The Sick Child” by Edvard Munch (1896) 18. “Madonna” by Edvard Munch (1895) 19. “Poppies Near VÃÂétheuil” by Claude Monet (1879) 20. “Haystacks (End of Summer)” by Claude Monet (1891) 21. “Water Lilies” by Claude Monet (1916) 22. “Starry Night” by Vincent van Gogh (1889) 23. “Cafe Terrace at Night” by Vincent van Gogh (1888) 24. “The Bedroom” by Vincent van Gogh (1889) 25. “Sunflowers” by Vincent van Gogh (1888) 26. “A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte” by Georges Seurat (1886) 27. “Bathers at AsniÃÂères” by Georges Seurat (1884) 28. “Young Woman in a White Hat” by Pablo Picasso (1901) 29. “Les Demoiselles d’Avignon” by Pablo Picasso (1907) 30. “Guernica” by Pablo Picasso (1937)
Epoch
The time period of Photorealism is the late 1960s to the present.
AI ART RESSOURCES (AKA, well Tools)
Helping tools -> predefined search links on other pages: