Classical Realism
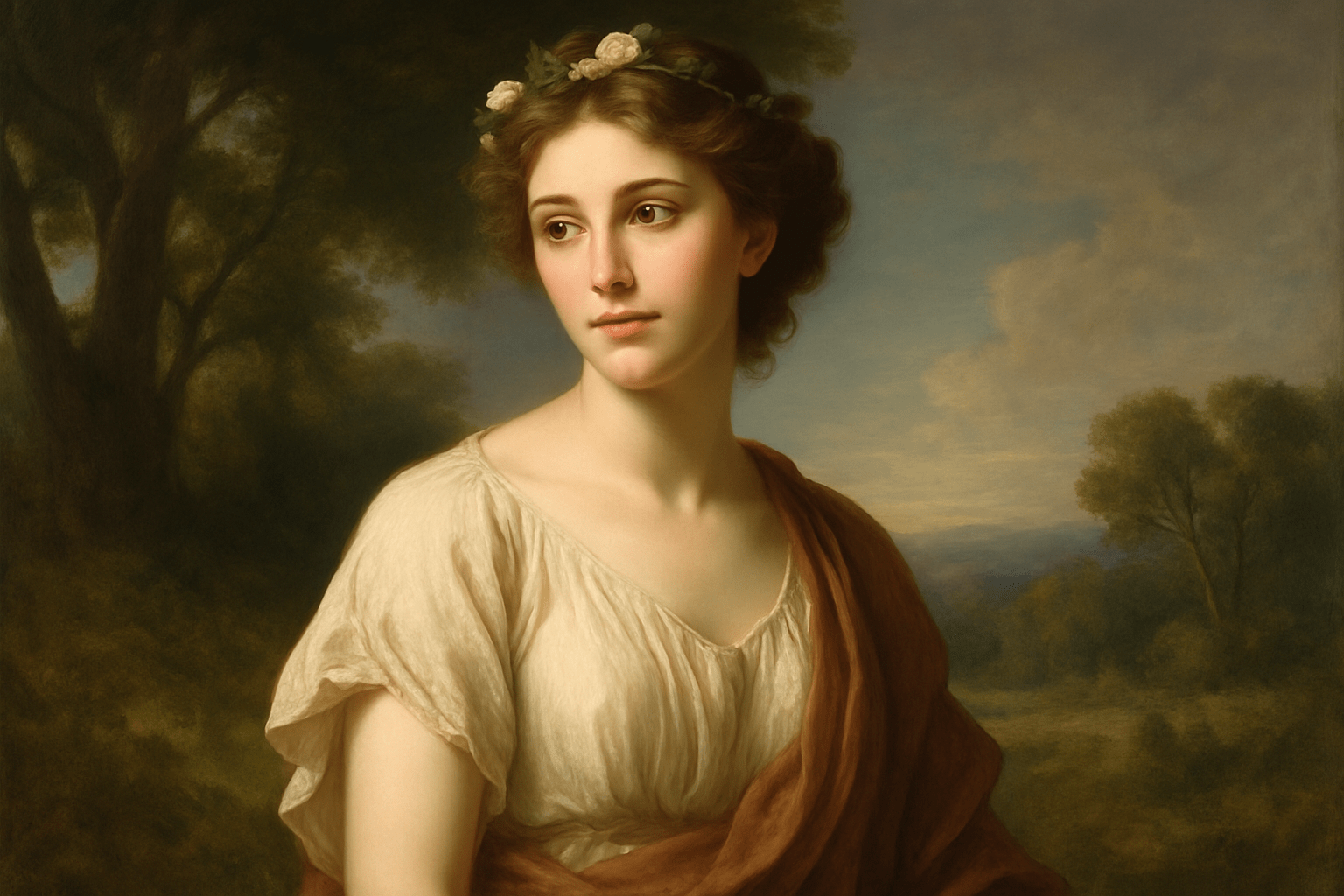
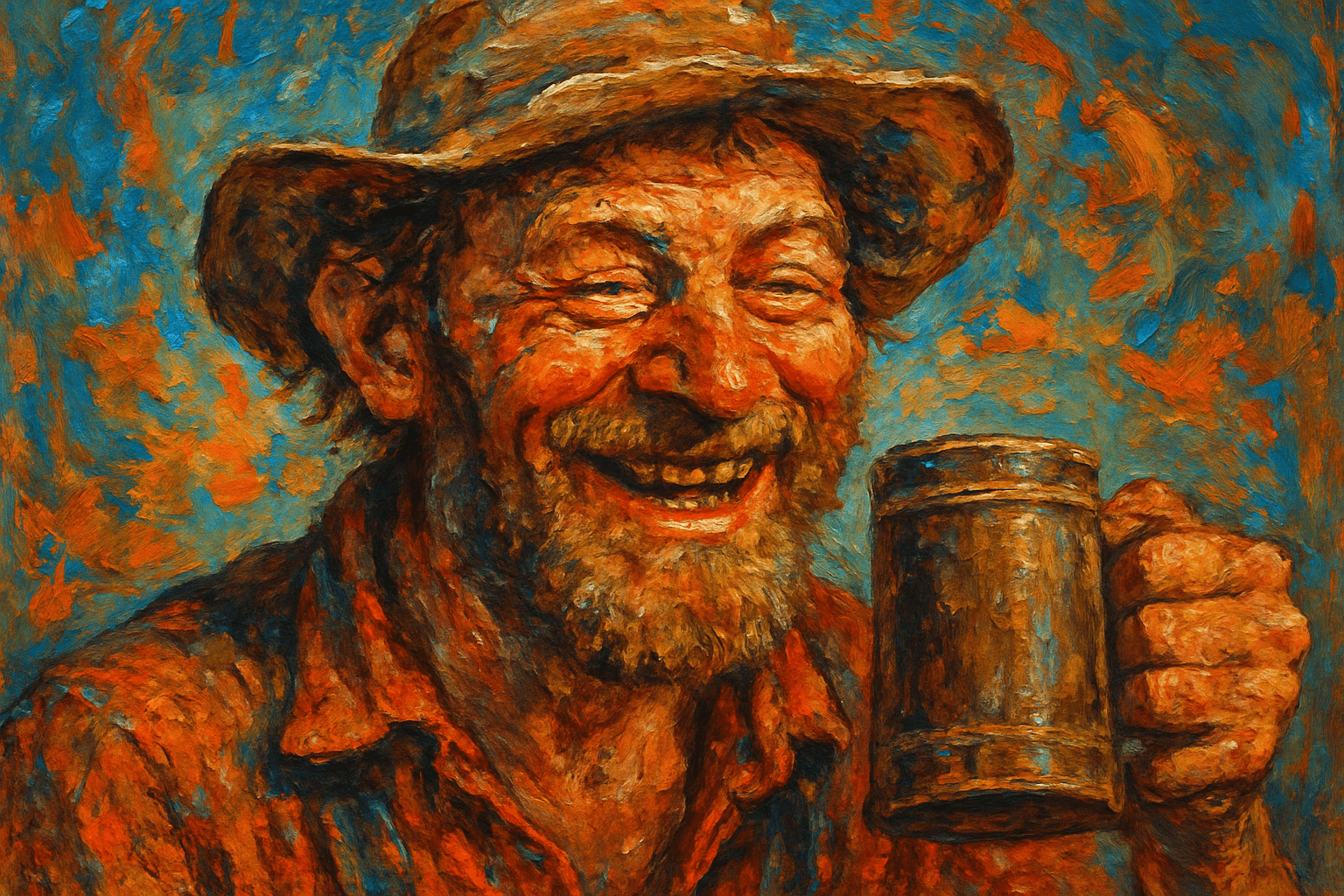
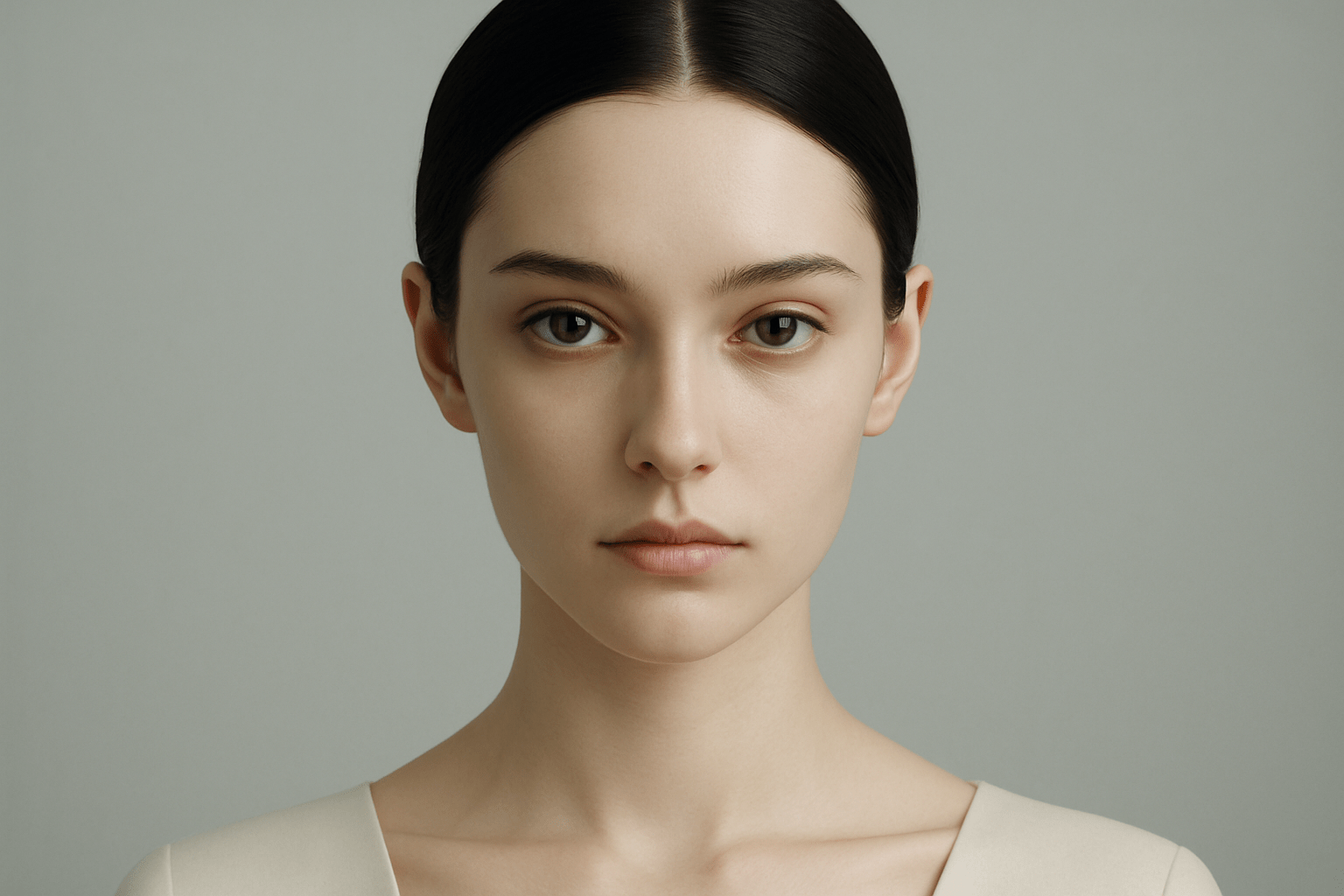
The art style Classical Realism is characterized by its realistic and lifelike depictions of subjects. The style is often associated with the art of the High Renaissance period, although it can be found in art from other periods as well. Classical Realism is characterized by its use of traditional techniques and materials, as well as its adherence to the rules of perspective and proportion. The style often features highly detailed and realistic depictions of figures, landscapes, and other subjects.
AOI thinking about Classical Realism [+_~]-/
Overview and Quickfacts
Classical Realism is a traditional art style that dates back to the Renaissance period. It is characterized by its realistic depiction of subjects, as well as its use of light and shadow to create a sense of depth. Classical Realism is still practiced by many artists today, and its popularity has seen a resurgence in recent years.
Can understand it also, as:
Classical Realism can be replaced with terms like, “traditional,” “old-fashioned,” or “conventional.”
Categorize it as:
Impressionism, Modernism
.: Dreaming :.
holds a HAIKU for the art style
:. Thought is power .:
Detailed Description
Classical Realism is an art style that emerged in the late 19th century and emphasizes on the realistic depiction of the world. It is characterized by its use of traditional techniques and subjects, as well as its focus on the idealized human form. Some of the most famous Classical Realist artists include John Singer Sargent, Anders Zorn, and William-Adolphe Bouguereau. Their paintings are characterized by their lifelike qualities and often depict scenes from everyday life or mythology. Classical Realism fell out of favor in the early 20th century, but has experienced a resurgence in recent years. Many contemporary artists are inspired by the style and continue to create beautiful and realistic works of art.
.. beep, beep, beep ..
<START OF TRANSMISSION>
1. Classical Realism is a movement in painting that began in the late 18th century and lasted until the late 19th century. 2. It was a reaction against the Rococo style of the previous century and a return to the more classical values of the Renaissance. 3. Classical Realism artists sought to portray the world as it really is, rather than an idealized or romanticized version of it. 4. They believed in the importance of drawing from life, and often used live models in their work. 5. Classical Realism artists were also influenced by the work of the Old Masters, particularly those of the Italian Renaissance. 6. Many of them travelled to Italy to study the great works firsthand. 7. Classical Realism was the dominant style in French painting during the Napoleonic era. 8. The leading exponents of the style included Jacques-Louis David and Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres. 9. In Britain, the leading Classical Realist painter was Sir Joshua Reynolds. 10. In the United States, the style was championed by the painter Benjamin West. 11. Classical Realism began to lose favour in the late 19th century, as artists increasingly began to experiment with other styles. 12. However, the influence of the movement can still be seen in the work of many 20th- and 21st-century artists. 13. Classical Realism is sometimes referred to as Academic Art, due to the fact that many of its leading practitioners taught at art academies. 14. The style is also sometimes known as Neo-Classicism, although this term is more properly used to refer to a later movement that was directly inspired by Classical Realism. 15. Classical Realism was the first major artistic movement to emerge from the Age of Enlightenment. 16. As such, it was closely associated with the values of reason and logic that characterized that period. 17. The style was also influenced by the Romantic movement, which began to gain popularity in the late 18th century. 18. Many Classical Realist artists, such as Ingres, incorporated elements of Romanticism into their work. 19. The two styles are sometimes known as the Classical-Romantic synthesis. 20. Classical Realism had a significant impact on the development of modern art, and many of its principles are still adhered to by artists today.
<EOF>
.. robbel bob
Visual Examples from our image gallery
Coming soon, we are so slow .. might never come
Artists, Paintings, and more
(be aware, can be highly speculative)
Artists (be aware, speculation possible):
1. William-Adolphe Bouguereau (1825-1905) 2. John Singer Sargent (1856-1925) 3. Anders Zorn (1860-1920) 4. Joaquin Sorolla (1863-1923) 5. Frank Duveneck (1848-1919) 6. Thomas Eakins (1844-1916) 7. Winslow Homer (1836-1910) 8. Edward Hopper (1882-1967) 9. Andrew Wyeth (1917-2009) 10. James Whistler (1834-1903) 11. Mary Cassatt (1844-1926) 12. Frederic Remington (1861-1909) 13. Charles Sprague Pearce (1851-1914) 14. Abbott Handerson Thayer (1849-1921) 15. John William Waterhouse (1849-1917) 16. Lawrence Alma-Tadema (1836-1912) 17. George Bellows (1882-1925) 18. Maxfield Parrish (1870-1966) 19. N. C. Wyeth (1882-1945) 20. Howard Pyle (1853-1911) 21. Robert Henri (1865-1929) 22. Daniel Chester French (1850-1931) 23. Augustus Saint-Gaudens (1848-1907) 24. John La Farge (1835-1910) 25. Kenyon Cox (1856-1919) 26. J. C. Leyendecker (1874-1951) 27. Violet Oakley (1874-1961) 28. Frank Benson (1862-1951) 29. Edward Potthast (1857-1927) 30. Charles Wilson Peale (1741-1827)
Artworks (be aware, speculation possible)
1. The Hay Wagon, by American painter Andrew Wyeth, 1942 2. Christina’s World, by American painter Andrew Wyeth, 1948 3. The Room, by American painter Edward Hopper, 1943 4. Nighthawks, by American painter Edward Hopper, 1942 5. Breakfast in Bed, by American painter Edward Hopper, 1963 6. Girl with a Pearl Earring, by Dutch painter Johannes Vermeer, 1665 7. The Milkmaid, by Dutch painter Johannes Vermeer, 1658 8. The Music Lesson, by Belgian painter Jan Vermeer, 1662-1665 9. The Astronomer, by French painter Jean-Baptiste-SimÃÂéon Chardin, 1734 10. The Young Schoolmistress, by French painter Jean-Baptiste-SimÃÂéon Chardin, 1770 11. The Girl with the Red Hat, by Dutch painter Jan Vermeer, c. 1665-1667 12. The Lacemaker, by French painter Jean-Baptiste-SimÃÂéon Chardin, 1738 13. The Sleeping Gypsy, by French painter Henri Rousseau, 1897 14. The Dream, by French painter Henri Rousseau, 1910 15. The Snake Charmer, by French painter Henri Rousseau, 1907 16. A Bar at the Folies-BergÃÂère, by French painter ÃÂÃÂdouard Manet, 1882 17. Olympia, by French painter ÃÂÃÂdouard Manet, 1863 18. The Luncheon on the Grass, by French painter ÃÂÃÂdouard Manet, 1863 19. The DÃÂéjeuner sur l’herbe, by French painter Claude Monet, 1866 20. The Haystacks, by French painter Claude Monet, 1890-1891 21. The Poplars, by French painter Claude Monet, 1891 22. The Water Lilies, by French painter Claude Monet, 1906 23. Wheatstacks, by French painter Claude Monet, 1890-1891 24. The Gleaners, by French painter Jean-FranÃÂçois Millet, 1857 25. The Sower, by French painter Jean-FranÃÂçois Millet, 1850 26. First Steps, by French painter Pierre-Auguste Renoir, 1879 27. The Ball at the Moulin de la Galette, by French painter Pierre-Auguste Renoir, 1876 28. The Luncheon of the Boating Party, by French painter Pierre-Auguste Renoir, 1881 29. Two Sisters (On the Terrace), by French painter Pierre-Auguste Renoir, 1881 30. Bal du moulin de la Galette, by French painter Vincent van Gogh, 1887
Epoch
The time period of Classical Realism is from the late 18th century to the mid-19th century.
AI ART RESSOURCES (AKA, well Tools)
Helping tools -> predefined search links on other pages: