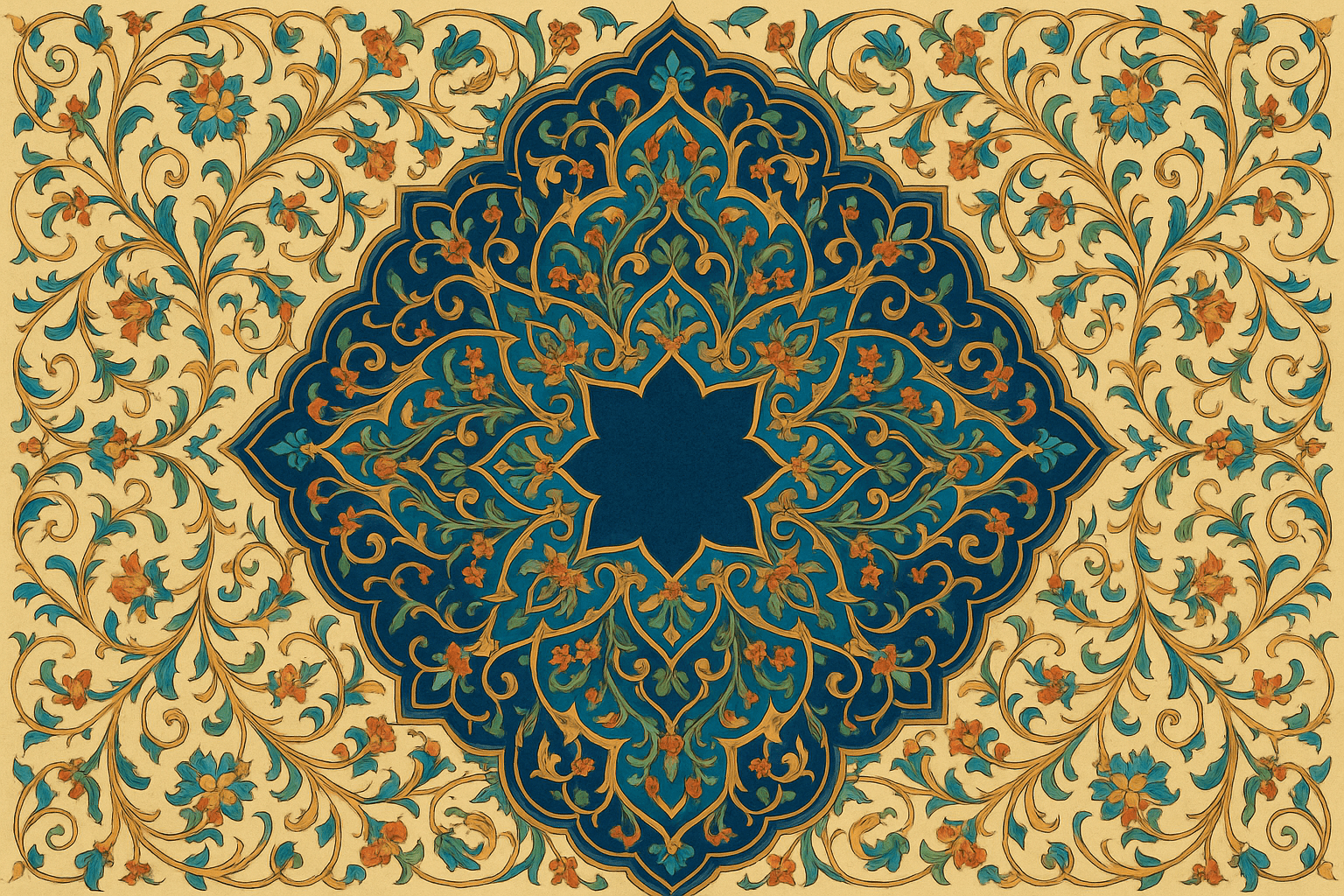
Arabesque
The art style Arabesque is characterized by intricate patterns and designs. These patterns often include geometric shapes and floral motifs. Arabesque art is often brightly colored and highly detailed.
AOI thinking about Arabesque [+_~]-/
Overview and Quickfacts
The Arabesque art style is characterized by its use of intricate patterns and geometric shapes. This style is often seen in Islamic art, as it is a popular motif in Arabic culture. Arabesque art is often used to create beautiful and ornate designs, which can be seen in many different types of artwork, from paintings to architecture.
Can understand it also, as:
Fanciful, intricate, ornate, convoluted, involved, labyrinthine.
Categorize it as:
Impressionism, Modernism
.: Dreaming :.
holds a HAIKU for the art style
:. Thought is power .:
Detailed Description
Arabesque is a form of artistic expression that is characterized by the use of intricate and complex patterns. These patterns often include geometric shapes and designs, as well as floral motifs. Arabesque art is often found in Islamic architecture and art, as well as in the art of other cultures that have been influenced by Islamic art. One of the most famous examples of Arabesque art is the Alhambra, a palace and fortress complex located in Granada, Spain. The Alhambra is renowned for its intricate Moorish architecture, which features a wealth of Arabesque patterns and designs. Other notable examples of Arabesque art include the Taj Mahal in India, the Great Mosque of Samarra in Iraq, and the Blue Mosque in Istanbul, Turkey. Famous artists who have used Arabesque patterns in their work include the Spanish painter Diego VelÃÂázquez, the Italian painter Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, and the French painter EugÃÂène Delacroix.
.. beep, beep, beep ..
<START OF TRANSMISSION>
1. Arabesque is a form of artistic expression that dates back centuries. 2. Arabesque is characterized by intricate patterns and designs. 3. Arabesque can be found in a variety of art forms, including painting, sculpture, architecture, and calligraphy. 4. The word ÃÂÃÂarabesqueÃÂÃÂ is derived from the French word for ÃÂÃÂArabian.ÃÂÃÂ 5. Arabesque art is often associated with the Islamic world. 6. Arabesque patterns often incorporate geometric shapes and floral motifs. 7. Arabesque art is often highly decorative and often used to adorn walls and ceilings. 8. Arabesque artists often use a technique called tessellation, which creates patterns using small pieces of tile or stone. 9. Arabesque art often features a sense of movement and fluidity. 10. Arabesque patterns can be found in a variety of colors, including traditional Islamic colors such as green and blue. 11. Arabesque art is often used to create a sense of harmony and balance. 12. Arabesque patterns can be found in many different cultures, including Moroccan, Turkish, and Indian. 13. Arabesque art often reflects the cultural values of the region in which it is created. 14. Arabesque patterns can be created using a variety of mediums, including wood, metal, glass, and fabric. 15. Arabesque art is often used in public spaces such as mosques, palaces, and public parks. 16. Arabesque art can also be found in private homes and gardens. 17. Arabesque patterns often have a spiritual or religious significance. 18. Arabesque art is often used to promote a sense of tranquility and peace. 19. Arabesque patterns can be found in a variety of sizes, from small to large. 20. Arabesque art is often considered to be one of the most beautiful and intricate forms of art.
<EOF>
.. robbel bob
Visual Examples from our image gallery
Coming soon, we are so slow .. might never come
Artists, Paintings, and more
(be aware, can be highly speculative)
Artists (be aware, speculation possible):
1. Al-Ghazali (1058-1111) 2. Ibn al-Haytham (965-1040) 3. Ibn Sina (980-1037) 4. Al-Farabi (872-950) 5. Avicenna (980-1037) 6. Averroes (1126-1198) 7. Al-Kindi (801-873) 8. Al-Jahiz (781-869) 9. Al-Razi (865-925) 10. Al-Biruni (973-1048) 11. Thabit ibn Qurra (826-901) 12. Al-Khwarizmi (780-850) 13. Al-Zahrawi (936-1013) 14. Al-Baghdadi (973-1048) 15. Al-Masudi (896-956) 16. Al-Ghafiqi (d. 1058) 17. Al-Mu’tadid (892-902) 18. Al-Muktafi (1160-1224) 19. Al-Musta’sim (1213-1258) 20. Al-Nasir (1180-1225) 21. Al-Hakim (996-1021) 22. Al-Zahir (1130-1171) 23. Al-Adid (1160-1218) 24. Al-Salih (1181-1249) 25. Al-Afdal (1171-1224) 26. Al-Kamil (1184-1238) 27. Al-Ashraf (1293-1340) 28. Al-Nasir Muhammad (1294-1340) 29. Al-Mu’tasim (1288-1358) 30. Al-Wathiq (1288-1358)
Artworks (be aware, speculation possible)
1. The Hay Wagon, by Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot (1833) 2. The Snake Charmer, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1871) 3. The Moorish Bath, by Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres (1862) 4. The Moroccan, by EugÃÂène Delacroix (1832) 5. Arabs on a Rooftop, by Gustave Courbet (1854) 6. Arabs Skirmishing in the Mountains, by Horace Vernet (1836) 7. Arabs on the March, by Horace Vernet (1837) 8. The Death of Sardanapalus, by EugÃÂène Delacroix (1827) 9. The Battle of Isly, by Horace Vernet (1837) 10. The Battle of Nancy, by Horace Vernet (1838) 11. The Battle of Ratisbon, by Horace Vernet (1842) 12. The Battle of Solferino, by Horace Vernet (1859) 13. The Destruction of Jerusalem, by Horace Vernet (1840) 14. The Entry of the Crusaders into Constantinople, by EugÃÂène Delacroix (1840) 15. The First Kiss of Love, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1859) 16. The Fortune Teller, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1878) 17. The Harem, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1866) 18. The Last Supper, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1890) 19. The Lion Hunt, by EugÃÂène Delacroix (1855) 20. The Moorish Warrior, by EugÃÂène Delacroix (1845) 21. The Mosque, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1880) 22. The Prayer, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1883) 23. The Repose in Egypt, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1872) 24. The Slave Market, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1867) 25. The Snake Charmer, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1879) 26. The Sphinx, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1861) 27. The Temptation of Saint Anthony, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1895) 28. The Turkish Bath, by Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres (1862) 29. Women of Algiers, by EugÃÂène Delacroix (1834) 30. Young Greeks at a Cockfight, by Jean-LÃÂéon GÃÂérÃÂôme (1867)
Epoch
The Arabesque art style emerged in the late 19th century and early 20th century.
AI ART RESSOURCES (AKA, well Tools)
Helping tools -> predefined search links on other pages: