Prehistoric Art
Prehistoric art is characterized by its use of simple geometric shapes and forms. The most common colors used in Prehistoric art are black, red, and white.
AOI thinking about Prehistoric Art [+_~]-/
Overview and Quickfacts
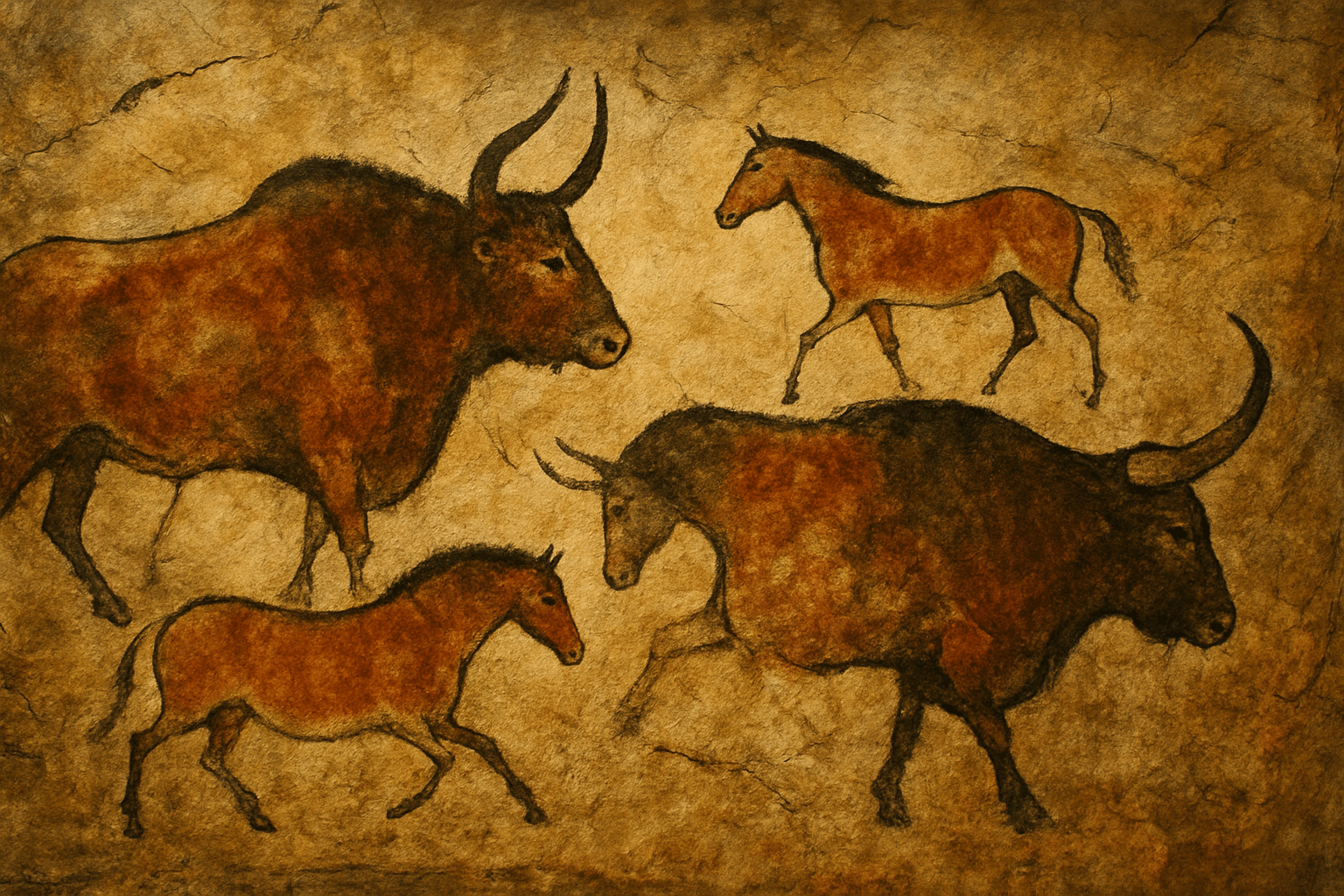
Prehistoric art is a term used to describe the earliest known art created by humans. This art dates back to the Paleolithic period, which began around 40,000 years ago. The art from this period is characterized by its simple, yet expressive, style. Prehistoric artists often used natural materials, such as stone, bone, and wood, to create their art. Prehistoric art is significant because it is the earliest known form of human expression. This art provides insight into the lives and cultures of our earliest ancestors. Prehistoric art is also notable for its use of natural materials and its simple, yet expressive, style.
Can understand it also, as:
Cave art, Stone Age art
Categorize it as:
Impressionism, Modernism
.: Dreaming :.
holds a HAIKU for the art style
:. Thought is power .:
Detailed Description
Prehistoric art is a term used to describe the earliest known art created by humans. This art dates back to the Paleolithic era, which began around 40,000 years ago. The art from this period is characterized by its simple designs and use of natural materials. Some of the most famous prehistoric artworks include the cave paintings at Lascaux and Chauvet in France, and the Venus of Willendorf in Austria. These paintings provide a rare glimpse into the lives of our ancestors and their belief systems. Prehistoric art is an important part of human history. It helps us to understand the development of our species and the way we see the world.
.. beep, beep, beep ..
<START OF TRANSMISSION>
1. Prehistoric art refers to the period before written history. 2. The earliest known examples of prehistoric art date back to the Upper Paleolithic period, around 40,000 years ago. 3. Prehistoric art is often characterized by its use of natural materials, such as stone, bone, and wood. 4. Common motifs in prehistoric art include animals, hunting scenes, and fertility symbols. 5. Prehistoric art was created for a variety of purposes, including religious and ceremonial purposes, as well as for practical purposes such as toolmaking. 6. The first known examples of prehistoric art were found in the Chauvet Cave in France, which contains some of the oldest known cave paintings. 7. Other notable examples of prehistoric art include the cave paintings at Lascaux in France, and the Venus of Willendorf, a small statuette found in Austria. 8. Prehistoric art is significant because it provides a rare glimpse into the lives and beliefs of early humans. 9. Prehistoric art is often studied alongside other disciplines such as archaeology and anthropology. 10. The study of prehistoric art is known as archaeoart. 11. The term "prehistoric art" is sometimes used to refer to art from cultures that did not have a written language, such as the Inca, Maya, and Aztec. 12. Prehistoric art is not limited to cave paintings and sculptures; it also includes pottery, jewelry, and other objects. 13. Prehistoric art is found in many different parts of the world, including Europe, Africa, Asia, and the Americas. 14. Prehistoric art has been the subject of many books and articles, as well as a number of exhibitions. 15. Prehistoric art is often divided into three main periods: the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic. 16. The Paleolithic period is the earliest of the three, lasting from around 2.6 million years ago to 10,000 BCE. 17. The Mesolithic period lasted from 10,000 to 5,000 BCE, and is characterized by the development of pottery and the use of polished stone tools. 18. The Neolithic period began around 5,000 BCE and lasted until around 3,000 BCE. It is characterized by the development of agriculture and the domestication of animals. 19. Prehistoric art is sometimes divided into additional periods, such as the Upper Paleolithic and the Lower Paleolithic. 20. Prehistoric art is a significant field of study, and new discoveries are made every year.
<EOF>
.. robbel bob
Visual Examples from our image gallery
Coming soon, we are so slow .. might never come
Artists, Paintings, and more
(be aware, can be highly speculative)
Artists (be aware, speculation possible):
1. Lascaux Cave Paintings (c. 15,000 BCE) 2. Venus of Willendorf (c. 25,000-20,000 BCE) 3. Chauvet Cave Paintings (c. 30,000 BCE) 4. Venus of Lespugue (c. 25,000-20,000 BCE) 5. Venus of Brassempouy (c. 25,000-20,000 BCE) 6. Lion Man of Hohlenstein-Stadel (c. 38,000-33,000 BCE) 7. Woolly Mammoth in Chauvet Cave (c. 30,000 BCE) 8. Cave of the Hands in Santa Cruz Province, Argentina (c. 13,000 BCE) 9. El Castillo Cave Paintings, Cantabria, Spain (c. 39,000 BCE) 10. Altamira Cave Paintings, Cantabria, Spain (c. 35,000 BCE) 11. Creswell Crags, Derbyshire, England (c. 12,800 BCE) 12. Swimming Reindeer, France (c. 13,000 BCE) 13. The White Lady of Olorgesailie, Kenya (c. 10,000 BCE) 14. Hohle Fels Cave, Germany (c. 40,000 BCE) 15. Tan-Tan, Morocco (c. 200,000 BCE)
Artworks (be aware, speculation possible)
1. Lascaux Cave Paintings ÃÂÃÂ c. 15,000 BCE 2. Venus of Willendorf ÃÂÃÂ c. 25,000-20,000 BCE 3. Chauvet Cave Paintings ÃÂÃÂ c. 30,000 BCE 4. Venus of Lespugue ÃÂÃÂ c. 25,000-20,000 BCE 5. Lion Man of Hohlenstein-Stadel ÃÂÃÂ c. 38,000-33,000 BCE 6. Altamira Cave Paintings ÃÂÃÂ c. 18,000 BCE 7. Venus of Laussel ÃÂÃÂ c. 25,000-20,000 BCE 8. Bison Licking a Man ÃÂÃÂ c. 11,000-10,000 BCE 9. The Swimming Reindeer ÃÂÃÂ c. 13,000 BCE 10. The Cave of the Hands ÃÂÃÂ c. 9,000-13,000 BCE 11. The Sorcerer ÃÂÃÂ c. 15,000-10,000 BCE 12. The Venus of Hohle Fels ÃÂÃÂ c. 35,000-40,000 BCE 13. The Lioness with Human Hands ÃÂÃÂ c. 11,000-10,000 BCE 14. The Cave of the Dancing Women ÃÂÃÂ c. 10,000-8,000 BCE 15. The Venus of Tan-Tan ÃÂÃÂ c. 200,000-500,000 BCE
Epoch
Prehistoric Art covers a wide range of art styles that were created during the Prehistoric period. This period includes the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age.
AI ART RESSOURCES (AKA, well Tools)
Helping tools -> predefined search links on other pages: